Packer: absent
Compilation date: 2021-09-03 12:04:44
- SHA1 hash: 595b5a7f25834df7a4af757a6f1c2838eea09f7b
Description
The trojan is written in C. The program contains several files, each of which is sequentially used by the trojan. The main task of the trojan is to decrypt the shellcode and execute it. The decrypted shellcode contains BackDoor.Whitebird.30, a module for bypassing UAC, and backdoor configuration.
Operating routine
The trojan folder contains the following files:
- mcupdui.exe - the executable file into which the malicious library is loaded using Hijacking DLL has a valid McAfee signature: 4F638B91E12390598F037E533C0AEA529AD1A371: CN=McAfee, Inc., OU=IIS, OU=Digital ID Class 3 - Microsoft Software Validation v2, O=McAfee, Inc., L=Santa Clara, S=California, C=US;
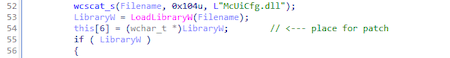
- McUiCfg.dll — downloader;
- mscuicfg.dat - encrypted shellcode;
- mcupdui.ini — configuration of trojan;
To move to the main malicious functionality, the Trojan modifies the process memory:
The instruction following the download of the malicious library is modified:
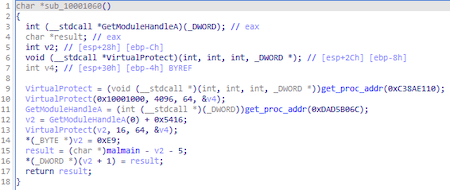
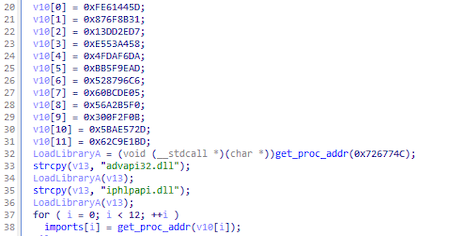
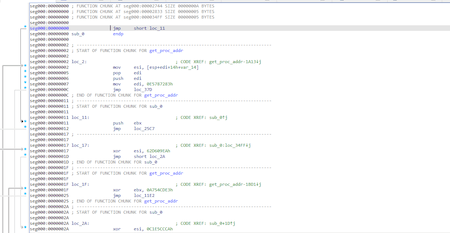
Trojan.Loader.891 finds all the functions it needs by hashes using the PEB (Process Environment Block) structure.
At the same time, the names of libraries and functions are hashed differently: library names are hashed as Unicode strings converted to upper case, and function names are hashed as ASCII strings without changing the case. The resulting two hashes are added together and then compared with the desired one.
[code]ror = lambda val, r_bits, max_bits: \
((val & (2 ** max_bits - 1)) >> r_bits % max_bits) | \
(val << (max_bits - (r_bits % max_bits)) & (2 ** max_bits - 1))
def hash_lib_whitebird(name: bytes) -> int:
a = name.upper() + b'\x00'
c = 0
for i in range(0, len(a)):
c = (a[i] + ror(c, 13, 32)) & 0xffffffff
# library name is a unicode string
c = (0 + ror(c, 13, 32))
return c
def hash_func_whitebird(name: bytes) -> int:
a = name + b'\x00'
c = 0
for i in range(0, len(a)):
c = (a[i] + ror(c, 13, 32)) & 0xffffffff
return c
Main functions of trojan are encrypted. When the function is called, it decrypts its code, and when it exits, it encrypts it back.
Main function:
Trojan.Loader.891 obtains the MAC addresses of all network interfaces on the computer. The trojan then reads data from the mscuicfg.dat file. If the last 6 bytes are zero, then it writes the first MAC address from the list into them and encrypts this file with the RC4 algorithm. In this case, the key is equal to the MAC address written to the file, the encrypted data is saved to the file mscuicfg.dat.
After that, in any way, the trojan reads the file again, sorting through each of the received MAC addresses until it finds the right one. The correctness of the decryption is checked by matching the last 6 decrypted bytes with the encryption key. Upon successful decryption, the trojan cuts them off and decrypts the file again using the RC4 algorithm, but takes the string mscuicfg.dat as the key. The received data is a shellcode with a configuration and a payload.
Shellcode
The shellcode is obfuscated with a lot of JMP instructions and each value is computed with a lot of SUB, ADD and XOR operations:
The principle of the shellcode is to decrypt the payload and then load it into memory for execution.
The last DWORD of the shellcode contains the OFFSET before the start of the payload.
Encrypted data at this stage:
For decryption, XOR with a dynamic key is used:
k = 0x37
s = bytearray()
for i in range(len(d)):
c = d[i] ^ k
s.append(c)
k = (k + c) & 0xff
The decrypted data contains an MZPE file with signatures replaced:
The decoded module is BackDoor.Whitebird.30. In addition, the module overlay contains an encrypted configuration and a module for bypassing UAC: